ELLIPSOID

| next surface | previous surface | 2D curves | 3D curves | surfaces | fractals | polyhedra |
ELLIPSOID

| Reduced Cartesian equation: with principal semi-axes When a = b or b = c: ellipsoid of revolution, or spheroid (otherwise, the ellipsoid is said to be scalene). - when a = b: oblate ellipsoid of revolution (shaped like a pebble or a flying saucer) - when b = c: prolate ellipsoid of revolution (shaped like a rugby ball or a cigar) - when a = b = c: sphere. Cartesian parametrizations: 1) 2) Mercator coordinates, change sin v to th v in 1) : 3) stereographic coordinates from the South pole: 4) parametrization the coordinate lines of which are the curvature lines: 5) parametrization the coordinate lines of which are the circles of the ellipsoid: Gaussian curvature: Mean curvature : Principal radii of curvature : - case a > b > c, with the above parametrization by the curvature lines :  . .
Area, symmetrical formula: Area, formula for a > b > c: Volume: |
The ellipsoid can be defined as a bounded quadric.
The ellipsoid is:
- the image by the scaling
of the circumscribed sphere S(O, a).
- the locus of a fixed point M of a variable line (D) three fixed points P,Q,R of which are constrained to move in three fixed planes secant two by two; the 3 semi-axes are then MP, MQ, MR.
The coordinate planes xOy, yOz, zOx are the principal planes of the ellipsoid, and their sections with the ellipsoid are its principal ellipses; two of these ellipses are enough to define the ellipsoid (and the ellipsoid is of revolution iff one of them is a circle:

The planar sections of the ellipsoid are ellipses,
which are similar when the planes are parallel.
When the ellipsoid is not of revolution, there exist
two directions of planes for which these sections are circular, which proves
that the ellipsoid is a doubly circled surface (see the 5th parametrization
above).
 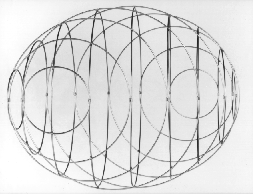
The two lattices of circles of the ellipsoid; the 4 limit circles are the umbilics. |

One of the lattices of circle placed horizontally. |
The la Hire method (or paper strip method) to construct the ellipse can be generalized as follow for the ellipsoid: if 3 fixed points on a line (D) are constrained to move on three planes secant 2 by 2, then any point on the line (D) describes an ellipsoid; for example, if a line (D) cuts yOz in A, zOx in B and xOy in Cand if M(x,y,z) on (D) is such that MA = a, MB = b and MC = c, then x²/a² + y²/b² + z²/b² = 1.
See the geodesics of the ellipsoid at Loria 3D p. 220.
Curvature lines of the ellipsoid, including the special cases of the three principal ellipses; the 4 singular points are the umbilics. They are "geodesic ellipses" with foci the umbilics (the sum of the geodesic distances to the umbilics is constant) |

Oblate ellipsoid of revolution; there are only two umbilics |

Prolate ellipsoid of revolution, same remark. |
| Elliptic domes are, more or less, half-ellipsoids.
Church San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane, Rome. |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| next surface | previous surface | 2D curves | 3D curves | surfaces | fractals | polyhedra |
© Robert FERRÉOL 2020