GAUSSIAN CURVE
| next curve | previous curve | 2D curves | 3D curves | surfaces | fractals | polyhedra |
GAUSSIAN CURVE

| Curve studied by de Moivre in 1718 and Gauss in 1809.
Karl Friedrich Gauss (1777 -1855): German astronomer, mathematician, and physicist. Other names: bell curve (of Gauss). |
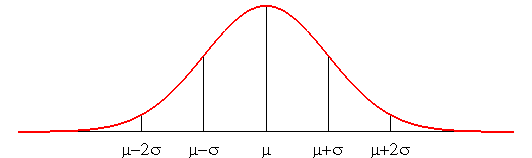
The area between the curve and the asymptote is equal to N; the area of the portion between m - s et m + s is approximately equal to 2/3 of N; between m - 2s and m + 2s it is approximately 96% of N. |
Cartesian equation: For example, the number |
The Gaussian curve is the curve of the density function of the normal distribution.
For ,
we get the Gaussian curve said to be "standard".
Do not mistake the bell curve of the Gaussian distribution with that of the Cauchy distribution, which is none other than a witch of Agnesi.
If we break away from the probabilistic aspect, the Gaussian
curve has the following characteristics:
| Cartesian equation: Area between the curve and the asymptote : |
 |
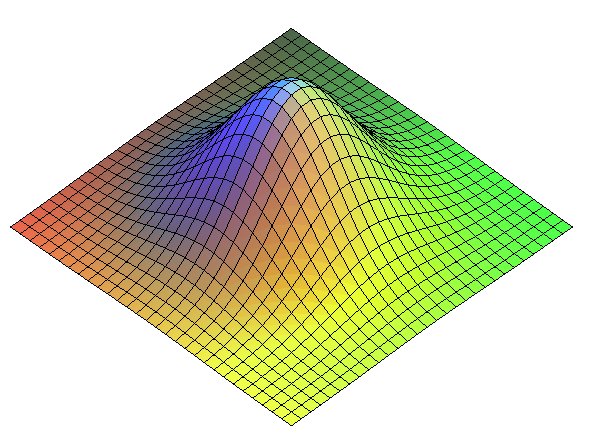
Associated surface of revolution.
| next curve | previous curve | 2D curves | 3D curves | surfaces | fractals | polyhedra |
© Robert FERRÉOL 2019