REVOLUTION OF THE SINUSOID
| next surface | previous surface | 2D curves | 3D curves | surfaces | fractals | polyhedra |
REVOLUTION OF THE SINUSOID

| Surface studied
in 2012 by G. Claeser and P. Calvache.
Homemade name, I'm am open to suggestions if you have a better name... |
| Cylindrical and Cartesian equations: Cartesian parametrizations: |
|
| 1) as a surface of revolution
of the sinusoid |
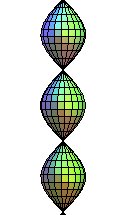 |
|
2) as a translation surface: |
|
| 3) as the surface of revolution of one of the previous
helices: |
|
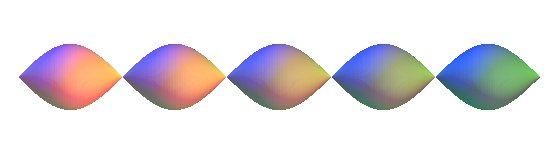
The revolution of the sinusoid is the surface of revolution obtained by rotation of a sinusoid around its axis of translation.
But it is remarkable that surface is also obtained by
translation
of a circular helix on a symmetric helix with respect to the axis (compare
to the right helicoid
which is obtained by translation of a helix on itself).
Therefore, it is also obtained by rotation of
a circular helix around a generatrix of the cylinder on which it is traced.
| The section of this surface by a cylinder tangent to
the axis and passing by the vertices is therefore composed of two symmetric
circular helices.
Remark (Lapalissade): these helices are the... helices of this surface of revolution.... |
|
| Obviously, there exist other curves obtained by revolution
of a sinusoid, for example: |
|
Do not mistake for the onduloid, and compare to the egg box.
See on this
page a polyhedron with diamond faces that approximates this surface.

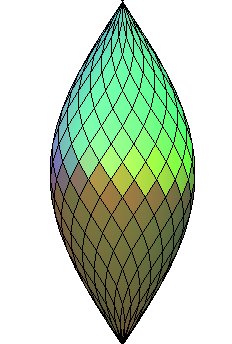
The Gherkin in London, was more or less built on this model.
| next surface | previous surface | 2D curves | 3D curves | surfaces | fractals | polyhedra |
© Robert FERRÉOL
2017